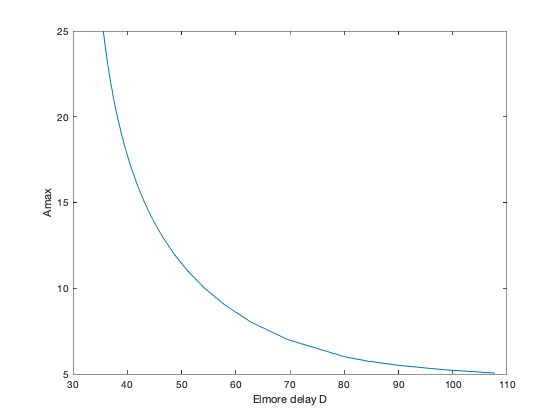
% Boyd, Kim, Vandenberghe, and Hassibi, "A Tutorial on Geometric Programming" % Boyd, Kim, Patil, and Horowitz, "Digital circuit optimization via geometric programming" % Written for CVX by Almir Mutapcic 02/08/06 % (a figure is generated) % % We consider the problem of finding optimal wire widths w_i % of N wire segments in an interconnect network, which will % minimize the critical Elmore delay, subject to limits on % wire widths and the total circuit area. We use a pi-model % for each wire segment. Problem can be formulated as GP: % % minimize D % s.t. w_min <= w <= w_max % area <= Amax % % where variables are widths w (and arrival times T that are used % to formulate the overall delay D expression). % % Important: We label root node as 1, and all the other nodes as % node_label_in_the_paper + 1 (due to Matlab's convention). % Also label nodes with increasing numbers downstream. %******************************************************************** % user supplied data (problem constants and tree topology) %******************************************************************** N = 6; % number of nodes (including the root node which is labeled as 1) % parent node array % specifies which node is a unique parent for node i (always have a tree) parent(1) = 0; % root node does not have a valid parent parent(2) = 1; parent(3) = 2; parent(4) = 3; parent(5) = 2; parent(6) = 5; % problem constants Rsource = 0.1; l = 1*ones(N-1,1); alpha = 1*ones(N-1,1); beta = 1*ones(N-1,1); gamma = 1*ones(N-1,1); % load capacitance at each node C1 = 10; C2 = 10; C3 = 10; C4 = 10; C5 = 10; Cload = [0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5]; % minimum and maximum width and area specification Wmin = 1; Wmax = 10; Amax = 15; %******************************************************************** % derived data (computed from user's data) %******************************************************************** % compute children cell array (evaluate who are children for each node) children = cell(N,1); leafs = []; for node = [1:N] children{node} = find(parent == node); if isempty(children{node}) leafs(end+1) = node; % leafs have no children end end %******************************************************************** % optimization (generating optimal tradeoff curve) %******************************************************************** disp('Generating the tradeoff curve...') Darray = []; for Amax = [5.05 5.25 5.5 5.75 6:25] % formulate the GP problem and solve it cvx_begin gp quiet % optimization variables variable w(N-1) % wire width variable T(N) % arrival time (Elmore delay to node i) % area definition area = sum(w.*l); % wire segment resistance is inversely proportional to widths R = alpha.*l./w; R = [Rsource; R]; % wire segment capacitance is an affine function of widths C_bar = beta.*l.*w + gamma.*l; C_bar = [0; C_bar]; % compute common capacitances for each node (C_tilde in GP tutorial) C_tilde = cvx( zeros(N,1) ); for node = [1:N] C_tilde(node,1) = Cload(node); for k = parent(node) if k > 0; C_tilde(node,1) = C_tilde(node,1) + C_bar(k); end; end for k = children{node} C_tilde(node,1) = C_tilde(node,1) + C_bar(k); end end % now compute total downstream capacitances C_total = C_tilde; for node = N:-1:1 for k = children{node} C_total(node,1) = C_total(node,1) + C_total(k,1); end end % objective is the critical Elmore delay minimize( max( T(leafs) ) ) subject to % generate Elmore delay constraints R(1)*C_total(1) <= T(1,1); for node = 2:N R(node)*C_total(node) + T(parent(node),1) <= T(node,1); end % area and width constraints area <= Amax; w >= Wmin; w <= Wmax; cvx_end % display and store computed values fprintf(1,' Amax = %5.2f delay = %3.2f\n',Amax,cvx_optval); Darray = [Darray cvx_optval]; end % plot the tradeoff curve figure, clf Amax = [5.05 5.25 5.5 5.75 6:25]; plot(Darray,Amax); xlabel('Elmore delay D'); ylabel('Amax');
Generating the tradeoff curve... Amax = 5.05 delay = 107.82 Amax = 5.25 delay = 98.33 Amax = 5.50 delay = 90.12 Amax = 5.75 delay = 84.35 Amax = 6.00 delay = 80.10 Amax = 7.00 delay = 69.64 Amax = 8.00 delay = 62.95 Amax = 9.00 delay = 58.10 Amax = 10.00 delay = 54.27 Amax = 11.00 delay = 51.17 Amax = 12.00 delay = 48.62 Amax = 13.00 delay = 46.50 Amax = 14.00 delay = 44.71 Amax = 15.00 delay = 43.19 Amax = 16.00 delay = 41.88 Amax = 17.00 delay = 40.76 Amax = 18.00 delay = 39.78 Amax = 19.00 delay = 38.92 Amax = 20.00 delay = 38.18 Amax = 21.00 delay = 37.52 Amax = 22.00 delay = 36.94 Amax = 23.00 delay = 36.43 Amax = 24.00 delay = 35.98 Amax = 25.00 delay = 35.59